How to address the growing security risk of IoT devices
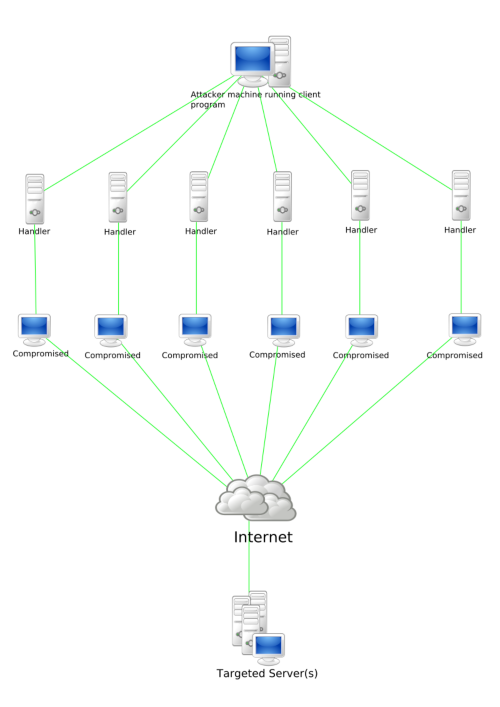
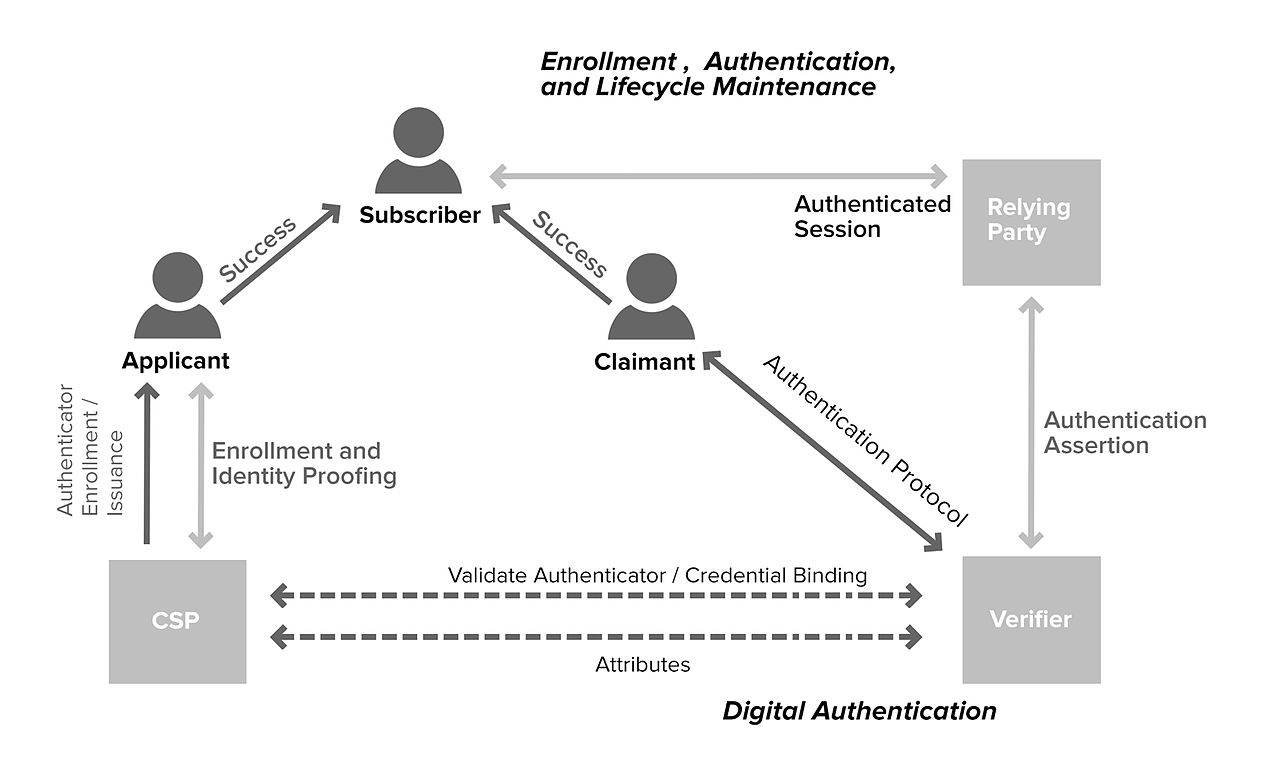
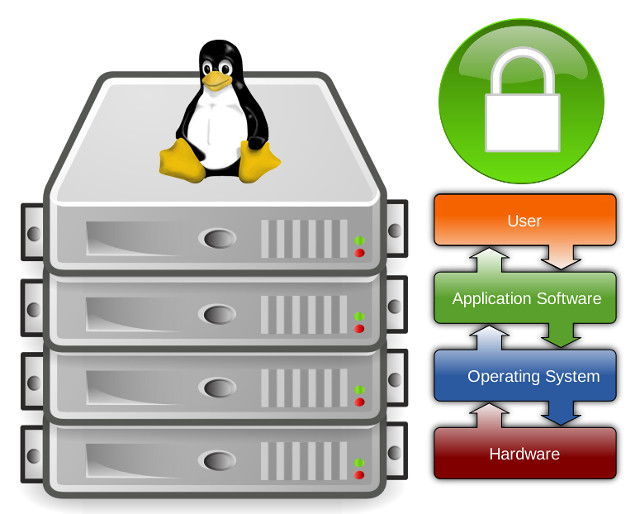
How to address the growing security risk of IoT devices The current Internet of Things (IoT) space comes with numerous security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities include weak authentication (IoT devices are being used with default credentials), unencrypted messages sent between devices, SQL injections and lack of verification or encryption of software updates. This allows attackers to easily intercept data to collect PII (Personally Identifiable Information), steal user credentials at login, or inject malware into newly updated firmware.